Quick jump:
- 1 Reciprocal Tariffs and the Trade Deficit
- 2 Current State of US Tariffs
- 3 Historical US Trade
- 4 Product-Specific Trade Balances
- 5 Sectoral Impact: Electronics, Transport, Chemicals, and Machinery
- 6 Market Reaction: A Tale of Volatility
- 7 Reciprocal Tariffs & S&P500 Reaction
- 8 Increased Volatility Due to Uncertainty
- 9 Political Impact on Markets (S&P 500 & VIX)
- 10 S&P 500 Reaction to Tariffs
- 11 VIX Reaction to Tariffs
- 12 Historical S&P 500 Reaction to Tariffs
- 13 Historical VIX Reaction to Tariffs
- 14 USD Rates Impact
- 15 USD-EUR Rates Impact
- 16 Conclusion
Since President Trump’s announcement of sweeping tariffs on “Liberation Day” in early April 2025, the global economic landscape has experienced significant turbulence. The initial shockwaves included a dramatic stock market crash, a sharp contraction in U.S. imports, and heightened geopolitical tensions. However, as of June 2, 2025, the situation has evolved: some tariffs have been paused or adjusted, legal challenges have introduced new uncertainties, and markets have shown signs of recovery.
This article delves into the multifaceted impacts of these tariffs, analysing how they have reshaped trade balances, influenced market dynamics, and prompted shifts in international relations over the past two months.
Reciprocal Tariffs and the Trade Deficit
The Trump administration introduced a reciprocal tariff formula targeting the U.S. trade deficit:
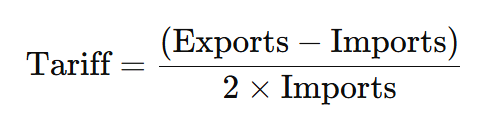
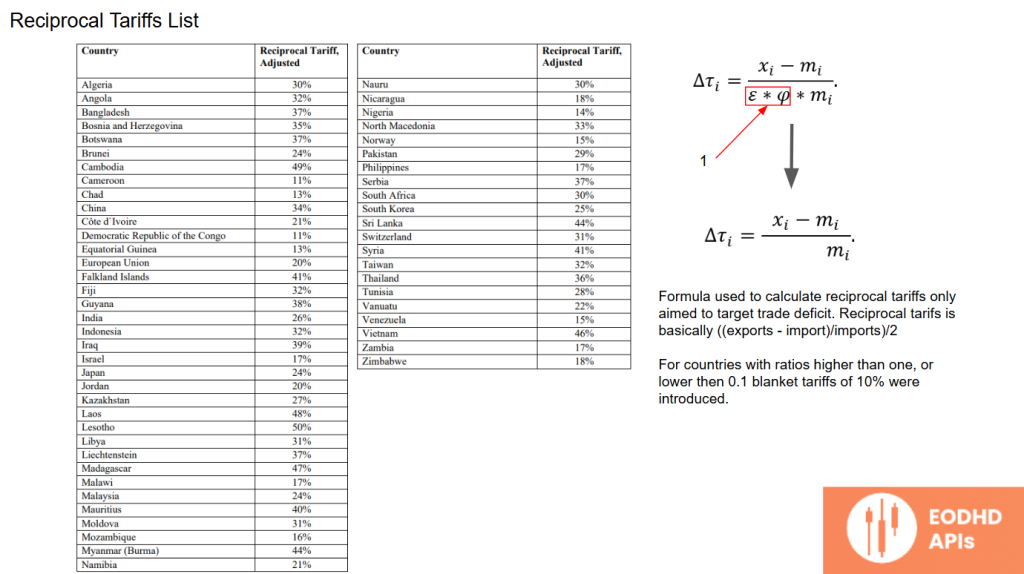
For countries with exceptionally high or low ratios, a blanket 10% tariff was imposed. While the intention was to rebalance trade, this approach oversimplifies complex trade dynamics, failing to account for supply chain intricacies and historical market trends.
Current State of US Tariffs
The White House strategy aims to reduce the trade deficit by applying a tariff based on half the trade balance ratio.
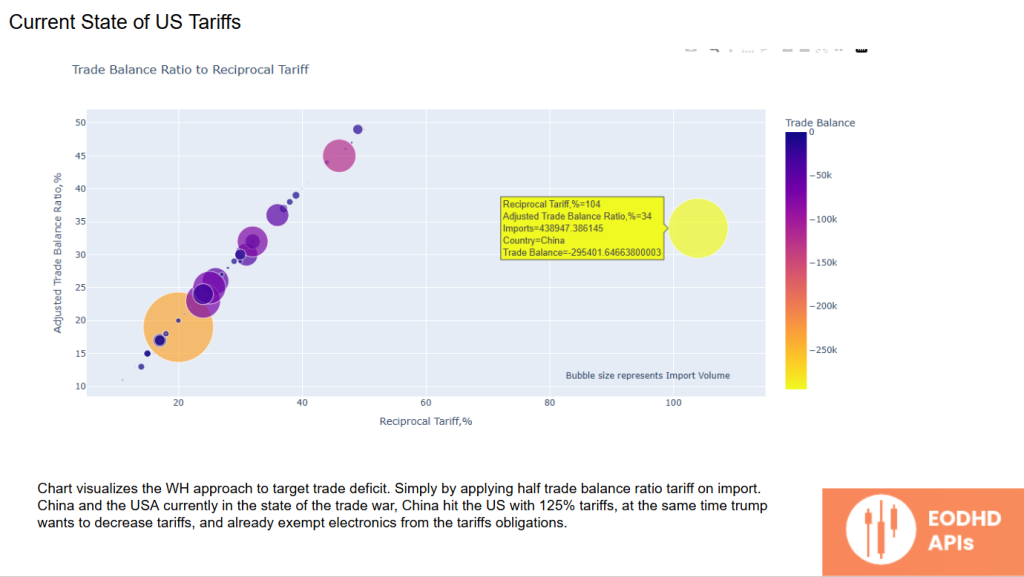
Currently, China and the US are engaged in a trade war, with China imposing 125% tariffs on US goods. Interestingly, the Trump administration exempted electronics from US tariffs, highlighting the administration’s attempt to minimize consumer impact while addressing trade imbalances.
Historical US Trade
Historical trade data reveals that while imports grew for decades, they have remained flat since 2022.
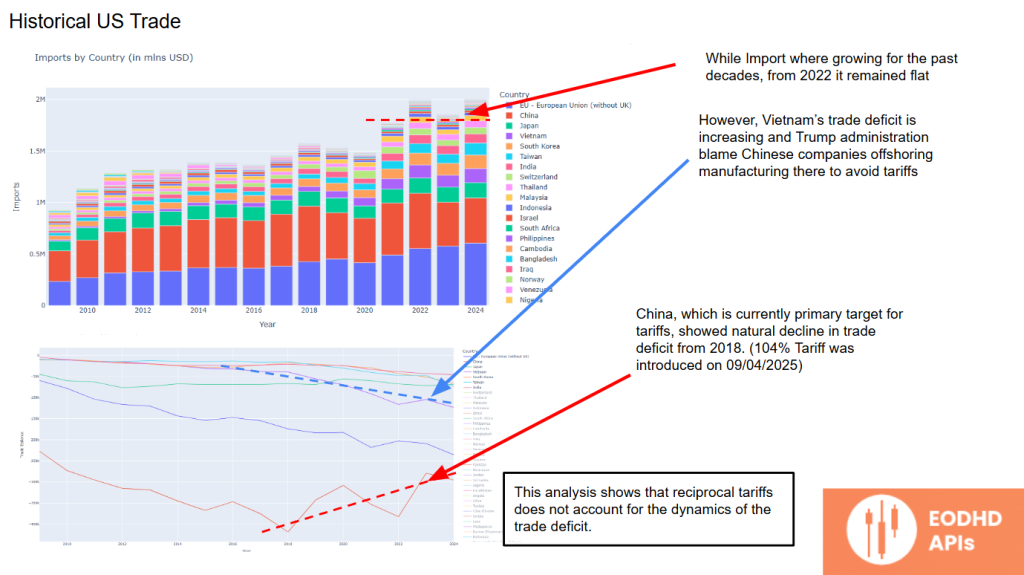
China’s trade deficit has naturally declined since 2018, even before the most recent tariffs. However, Vietnam’s trade deficit is rising — Trump officials blame Chinese firms relocating production to Vietnam to circumvent tariffs. This insight suggests that reciprocal tariffs may not effectively address trade deficit dynamics.
Product-Specific Trade Balances
A sectoral breakdown shows that while the overall US-China trade balance remained stable in key categories, computers and electronics have seen a declining balance since 2019.
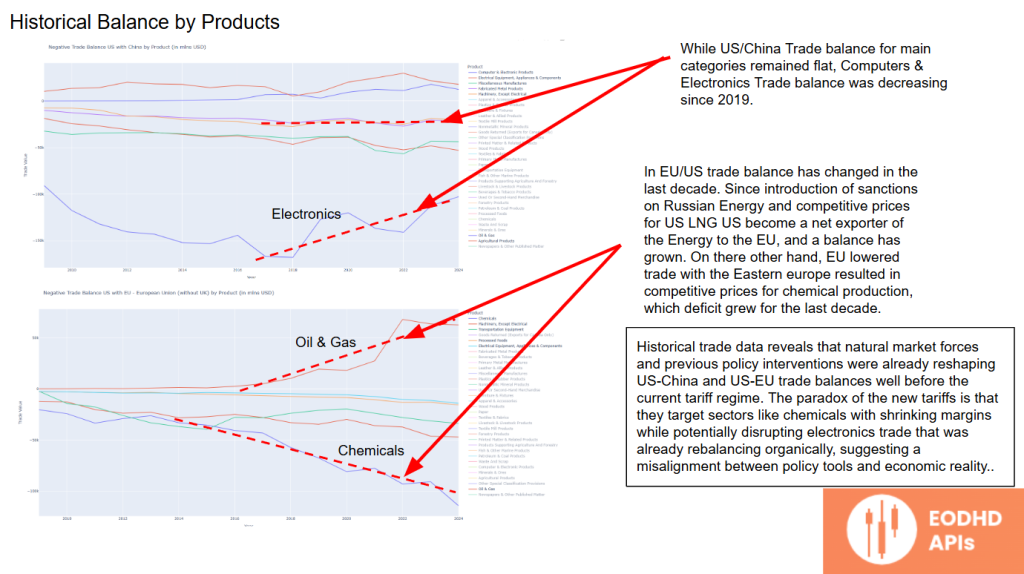
In the US-EU context, sanctions on Russian energy and the emergence of competitive US LNG exports have made the US a net energy exporter. At the same time, the EU’s decreased trade with Eastern Europe has led to competitive chemical production, deepening the US trade deficit in chemicals.
Sectoral Impact: Electronics, Transport, Chemicals, and Machinery
The US import/export profile shows that electronics, transport, chemicals, and machinery are among the most impacted categories by tariffs.
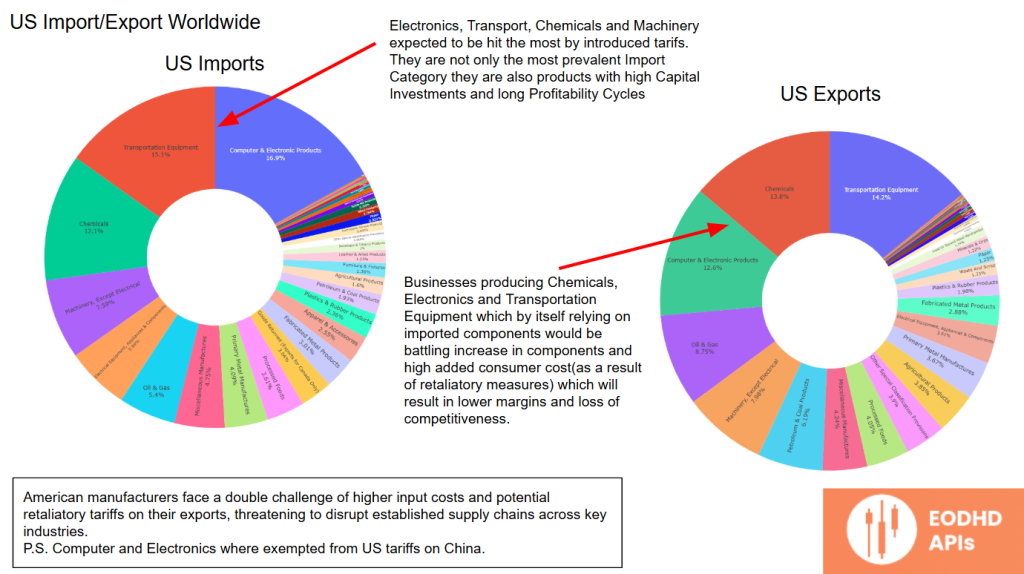
These industries involve significant capital investments and long profitability cycles, making them particularly vulnerable to tariff-related disruptions.
Businesses producing chemicals, electronics, and transportation equipment rely heavily on imported components. With tariffs in place, these companies face higher input costs and potential retaliatory tariffs on their exports.
Market Reaction: A Tale of Volatility
Following Trump’s announcement of tariffs on Liberation Day, the stock market has declined, with all sectors showing a 12% average drop.
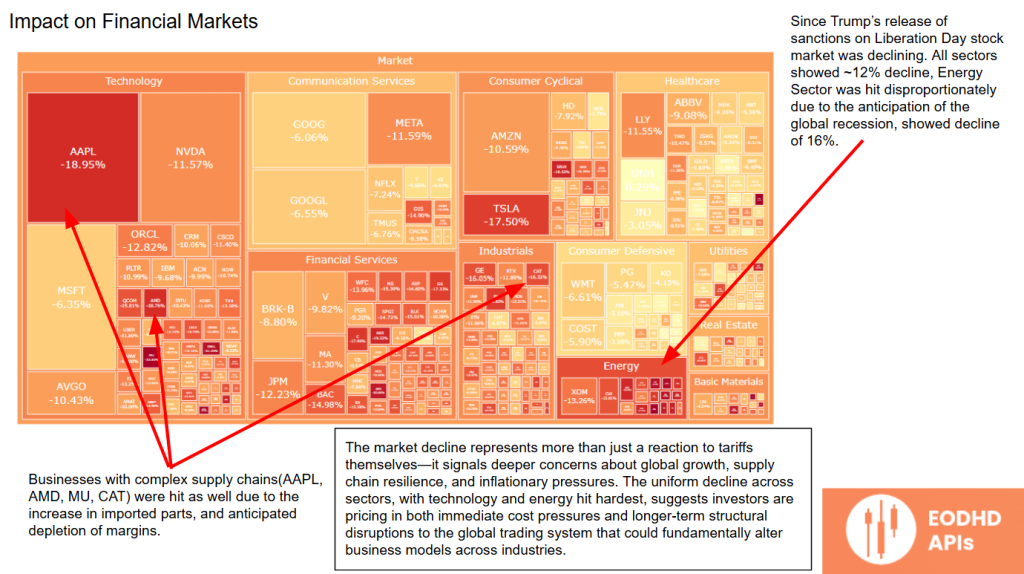
The energy sector has been hit especially hard (-16%) as fears of a global recession grow. Companies with complex supply chains (e.g., Apple, AMD, Caterpillar) have also been affected due to higher component costs and fears of shrinking margins.
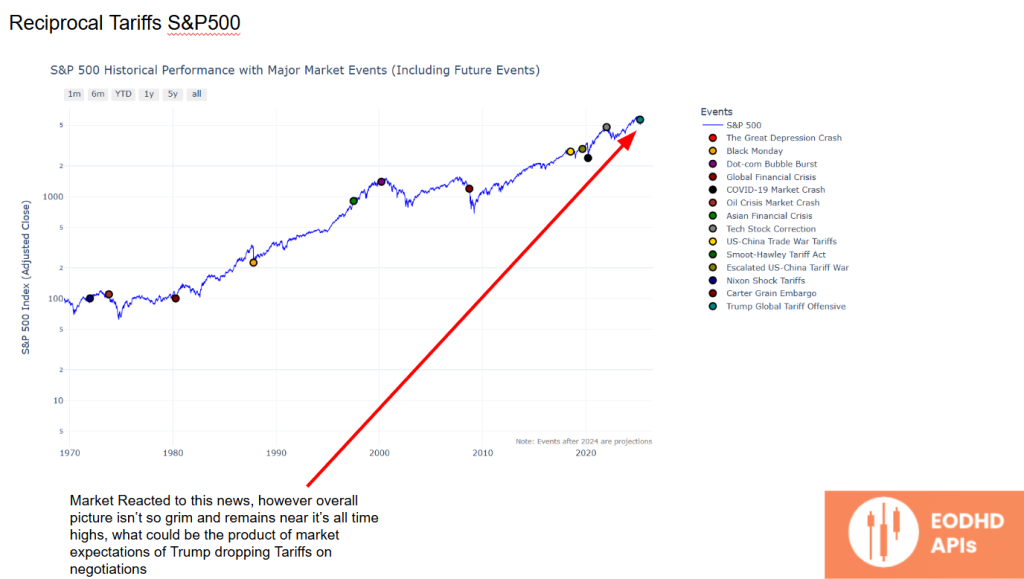
Reciprocal Tariffs & S&P500 Reaction
Despite the initial shock, the S&P 500 remains near historical highs — likely due to market expectations that Trump may roll back tariffs during negotiations.
Increased Volatility Due to Uncertainty
Trump’s tariff tactics have increased market volatility, as shown in the VIX index.
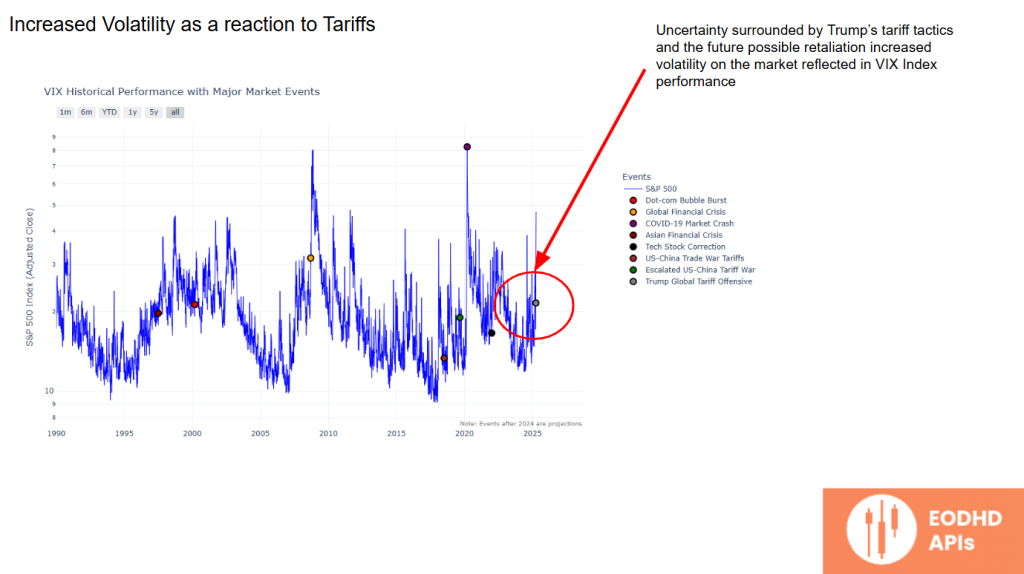
Uncertainty around potential retaliatory measures and tariff adjustments has driven sudden price swings, leaving investors on edge.
Political Impact on Markets (S&P 500 & VIX)
The political timeline from 2024 to 2025 shows how market volatility closely tracks political events:
- Trump’s tariff announcement in April 2025 caused a major market drop.
- The VIX spiked during this period, reflecting investor anxiety.
- When Trump froze tariffs, markets rebounded sharply.
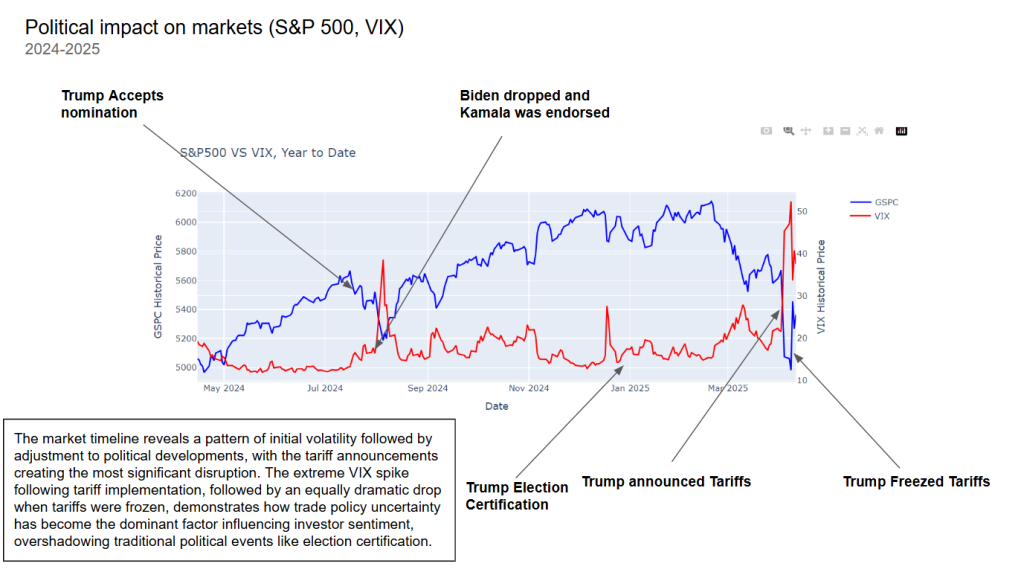
This pattern underscores how markets are more sensitive to trade policy uncertainty than to traditional political milestones, like elections or nominations.
S&P 500 Reaction to Tariffs
Specific dates reveal the intensity of market reactions:
- December 17: Electoral College certification of Trump’s victory triggered a 2.9% drop in the S&P 500.
- April 2: Trump’s tariff announcement caused a 4.8% one-day drop.
- April 9: Trump’s freeze on tariffs reversed the trend, sparking a record-setting 9.5% one-day rebound.
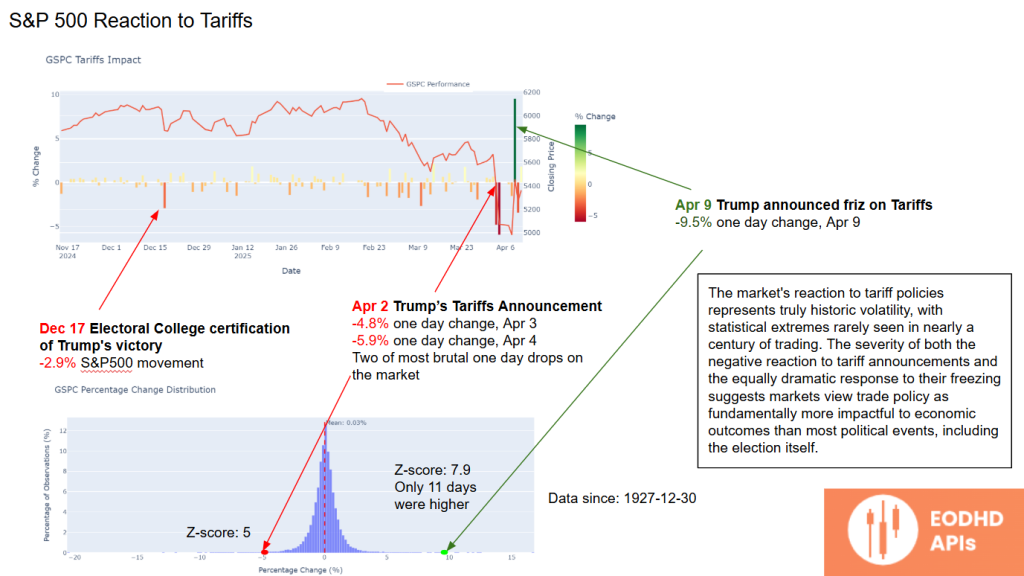
The market’s reaction to tariffs has reached historically high volatility levels, with Z-scores rarely seen since 1927. This highlights how trade policy has become a primary driver of market sentiment.
VIX Reaction to Tariffs
The VIX index tells a similar story:
- April 3-4: The VIX surged by 39% and 50% respectively.
- April 9: Trump’s tariff freeze caused a record 35% one-day drop in the VIX — an extreme move signalling relief among investors.
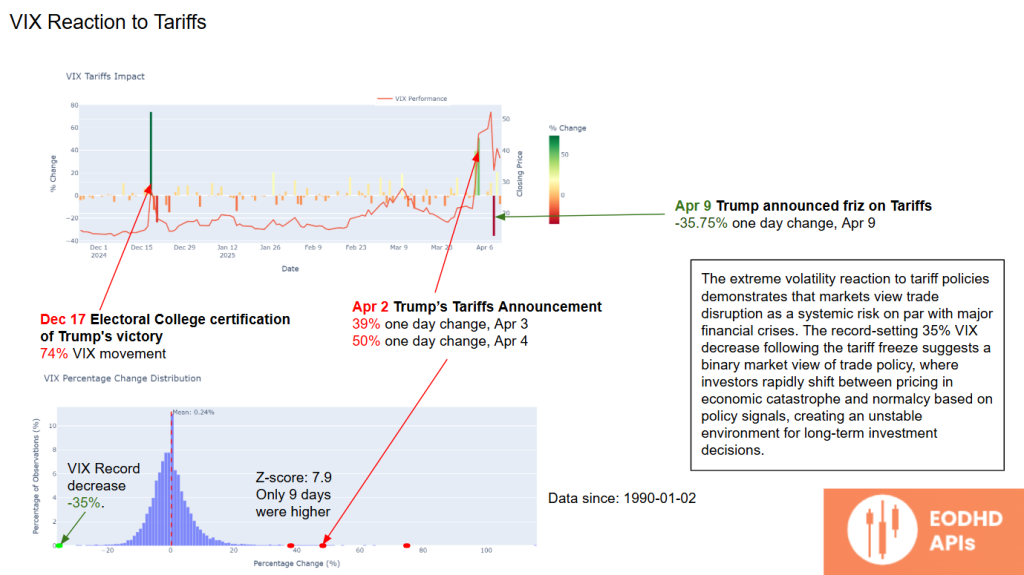
This volatility shows that markets view trade policy uncertainty as a systemic risk comparable to major financial crises.
Historical S&P 500 Reaction to Tariffs
Historically, markets tend to absorb tariff shocks within weeks and then revert to previous trends.
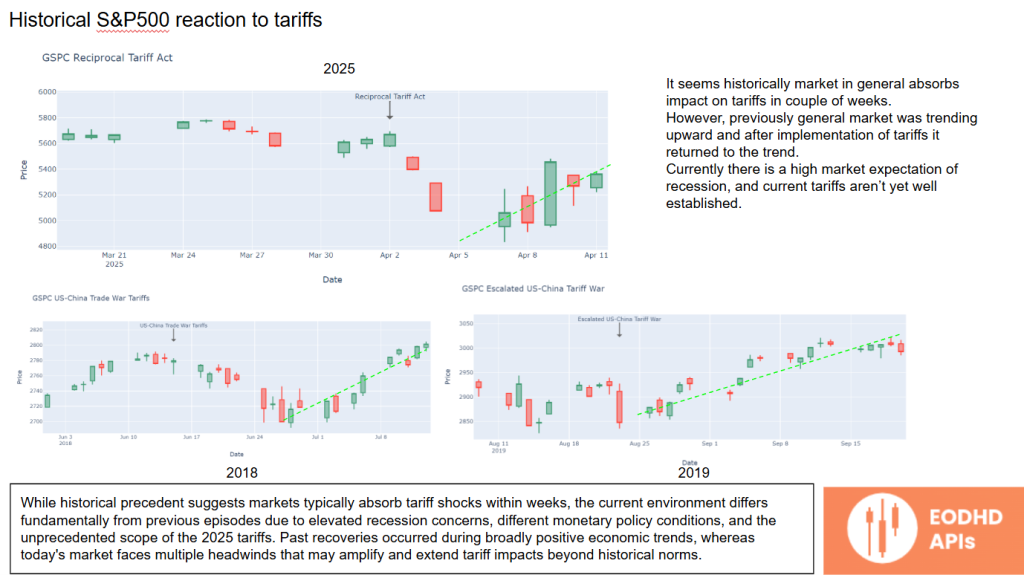
However, the current environment is different, with elevated recession fears, tighter monetary policy, and unprecedented tariff scope. These factors may amplify tariff impacts and prolong recovery times.
Historical VIX Reaction to Tariffs
The VIX historically shows that once tariffs are fully implemented, market volatility usually subsides.
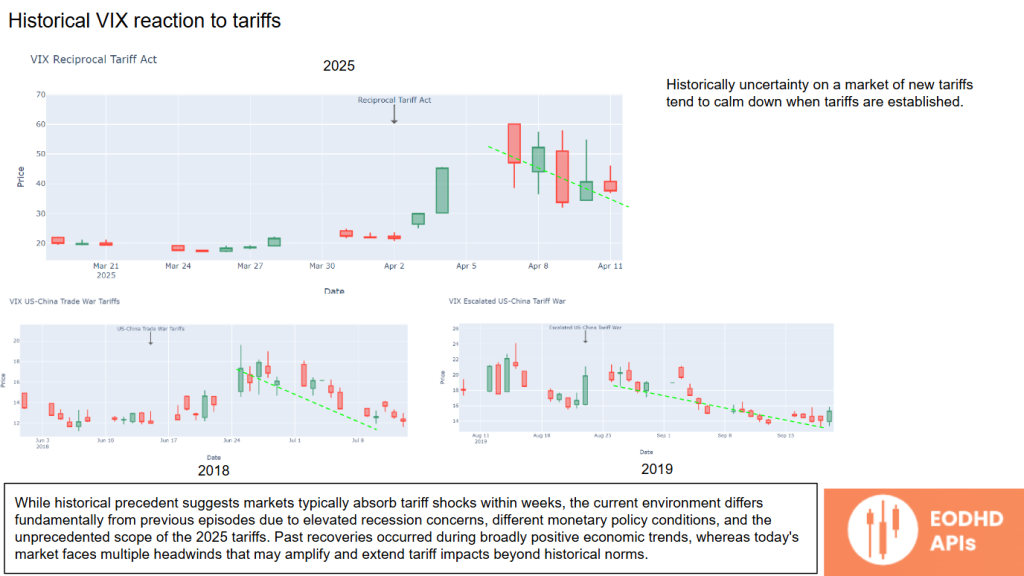
But the current cycle shows extended uncertainty due to global economic headwinds and policy unpredictability.
USD Rates Impact
Historically, the USD tends to strengthen during periods of high market volatility because it’s considered a safe haven. But the 2025 reciprocal tariffs have broken this pattern.
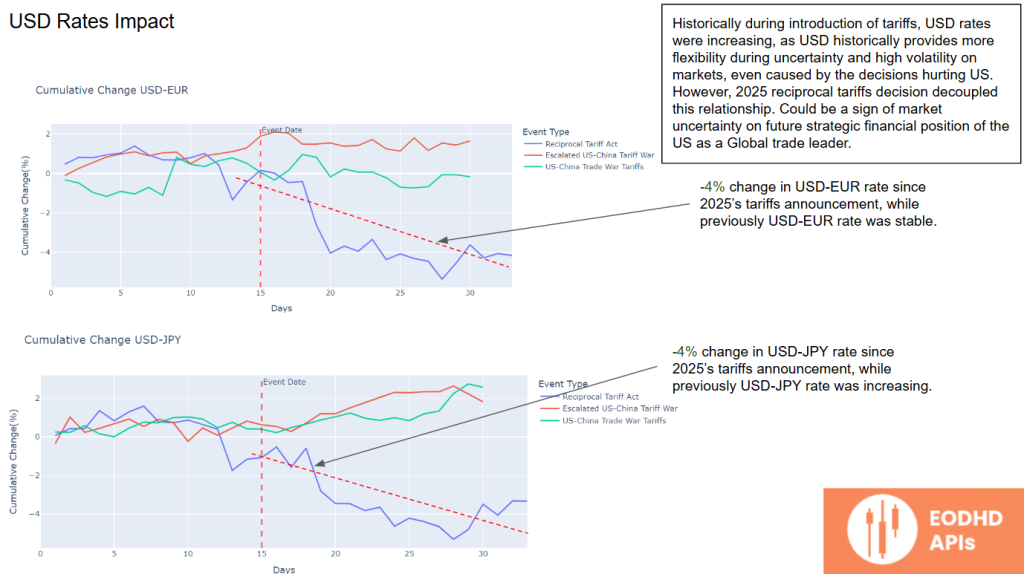
The USD has weakened by 4% against both the euro and the yen, reflecting market uncertainty about America’s strategic position as a global trade leader.
USD-EUR Rates Impact
The USD-EUR exchange rate has fallen by 6% over three weeks since the tariffs were announced, defying historical patterns where the USD typically strengthens during trade disputes.
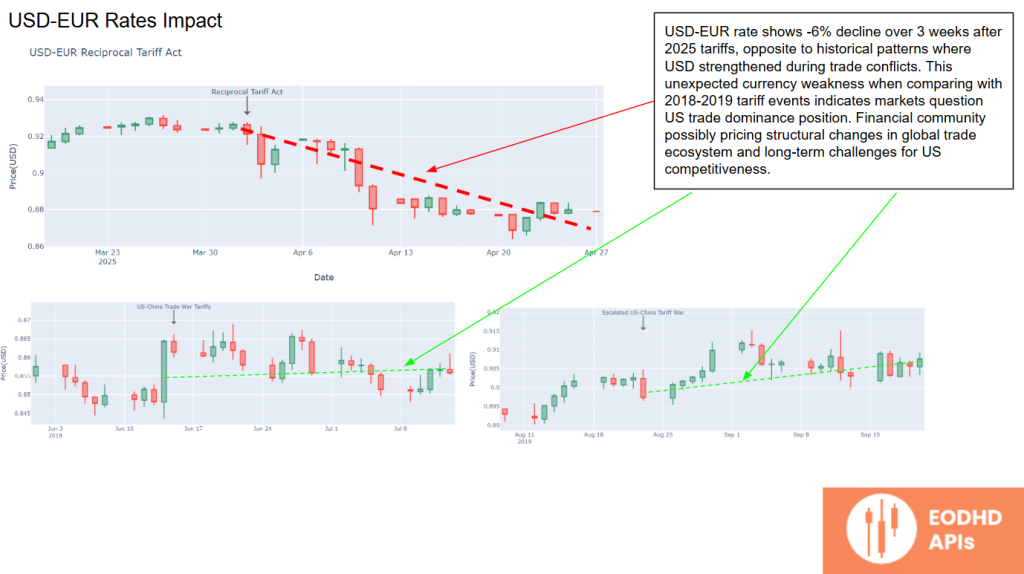
This suggests investors are reassessing the US’s long-term competitiveness in the global economy.
Conclusion
Two months after the implementation of President Trump’s tariffs, the global economy continues to grapple with their far-reaching effects. While the U.S. trade deficit narrowed significantly in April, this was largely due to a steep decline in imports rather than a surge in exports. Legal challenges have added layers of complexity, with courts temporarily halting and then reinstating certain tariffs, leaving businesses in a state of uncertainty. Markets have partially rebounded, yet sectors like private equity and retail remain under pressure, and consumers face rising prices on various goods. As the administration navigates ongoing negotiations and potential policy adjustments, stakeholders must remain vigilant, adapting to an economic environment marked by volatility and rapid change.
